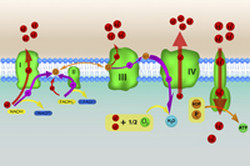
Dissecting the components of respiration
Cells obtain the energy required for most of their functions through an intricate process known as oxidative phosphorylation. This process converts the transfer of electrons between the mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) complexes – known as respiration – into the production of ATP, the cell's energy currency. The scope of the EU-funded 'Mitochondrial respiratory chain assembly' (MRCA) project was to study the mechanism of assembly of the MRC complexes especially complexes I and III. MRC complexes are found in mitochondria and consist of various subunits. Complex I is the largest of the MRC enzymes and contains 44 subunits, seven of which are encoded by the mitochondrial genome. To discover the assembly factors necessary for the process, scientists mutated the genes encoding the different subunits in mouse cells. They identified five distinct entry points in the process of MRC assembly where the seven subunits joined the assembly intermediates. Similarly, to examine the assembly of Complex III, researchers again studied the individual subunits and assembly factors through mutation or labelling. They delineated the process of subunit assembly and also identified how mutations of the mitochondrial MT-CYB subunit impair Complex III assembly. Overall, the findings of the MRCA study provided for the first time evidence on the assembly of the MRC in mammalian cells. The outcome of various MRC complex deficiencies is devastating, with multi-organ dysfunction, retardation and atrophy. In this context the outcome of the MRCA work helps to further understand the process of complex assembly and the role of accessory proteins.