Applications of 3D printing to help reducing maintenance, repair and overhaul costs for the air transport sector
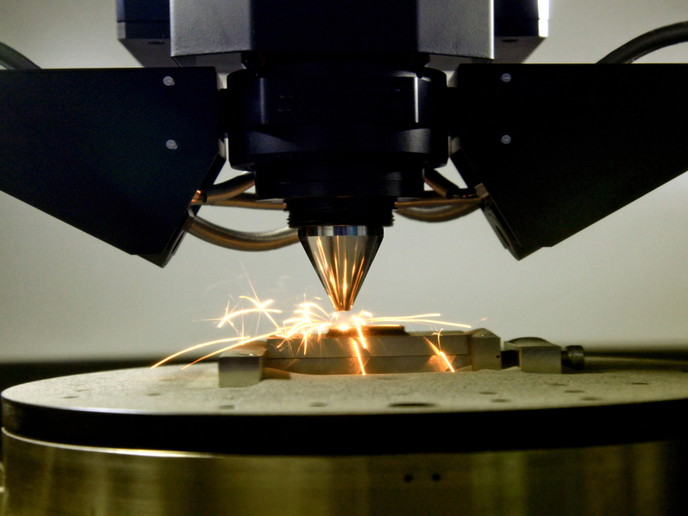
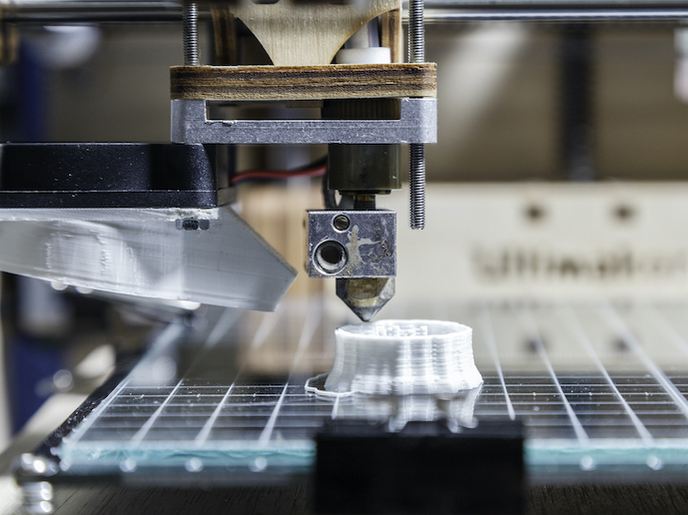
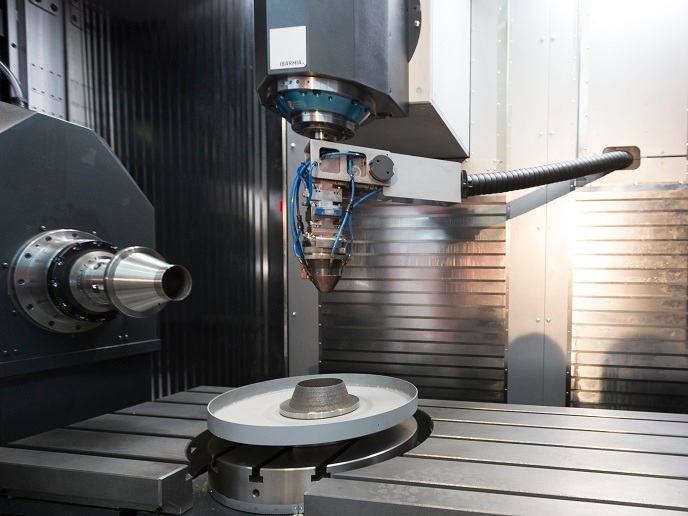
AM, which sequentially adds layers of material according to specifications in a computer-aided design file, has progressed tremendously since its inception for small batches of custom-designed parts. The EU-funded REPAIR(opens in new window) (Future repair and maintenance for aerospace industry) project set out to reduce the maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) costs in the aerospace industry through AM with less waste and a shorter lead time. Condition monitoring and predictive health management concepts were adapted to AM parts triggering the MRO process, estimating remaining useful lifetimes of parts and facilitating demand driven scheduling. REPAIR extended an existing MRO workflow management system and significantly enhanced this software by integrating various new IT components. In this way, the complete MRO process is supported by one integrated IT system architecture that boosts automation and cuts lead time and costs. To adapt the AM technology to the needs of aerospace, project partners developed a high batch repair using a special designed clamping device that enables the repair of many identical metal parts with an integrated in situ quality system. They also developed a 5-axis direct metal deposition machine, integrating the additive process with scanning and milling tools for repairing spare parts. The accompanying control software allows for the semi-automated analysis of defects, calculation of 3D layers and all manufacturing operations. The 5-axis system enables the machine to build up structures on uneven surfaces. As a result, the effort for pre- and post-processing broken spare parts can be significantly reduced. To be able to provide high-quality parts by AM and fully exploit the technology's potential, the REPAIR team performed extensive research into the testing of factors for surface, accuracy and part quality to determine optimised parameters and to ensure reliability. Among others, qualification and certification procedures were defined informing many related initiatives. A quality assurance information technology (IT) component was specified and integrated in the technological management platform. Lastly, researchers identified new business models both for the exploitation of the full solution and the individual components and industrial systems developed. The REPAIR team delivered a roadmap for its continued development. REPAIR technology promises numerous benefits, including a significant reduction in MRO costs and time, job creation, reduction of scrap and energy consumption, and enhanced aircraft safety. Innovative application of AM to on-site maintenance and repair is an idea ready to take flight.