Computer-aided engineering to protect composite aircraft from lightning
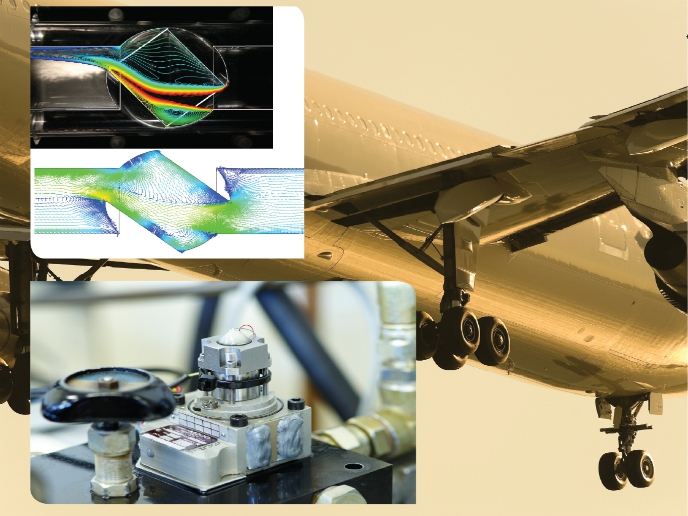
Over the last few years there has been a sharp increase in the demand for composite materials within new aircraft mainly due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. However, by increasing their fraction, challenges regarding electrical conductivity have arisen, such as lightning strike protection, static discharge and interference shielding. Given that composite materials have poor electrical conductivity, there is need for a dedicated conductive current return pathway such as an almost equipotential electrical network (ALEEN). A new modelling method enabled modelling the effects of lightning on cable-harness configurations installed aboard aircraft equipped with ALEEN. Within the project ARROW(opens in new window) (Aircraft lightning threat reduction through wiring optimization), researchers used numerical analysis and computer-aided engineering (CAE) tools to calculate the current and voltage at equipment level induced by a lightning strike. Accurate electromagnetic characterisation enabled the proper design of electrical systems such as an electrical wiring interconnection system without the need for repeated bread boarding. ARROW's analysis tool provides accurate modelling of ALEEN parts and complex 3D shapes, also including composite parts that have finite conductivity. Impedance, skin and proximity effects in expanded foils on composite layers are also taken into account. The newly developed CAE tool implements a set of pre- and post-processing as well as management functionalities suited to input the modelling data and prepare the electromagnetic model. Even if conducting an electromagnetic analysis on a model comprising all aircraft structures and the wires is theoretically possible, a hybrid field-to-wire coupling procedure can enable use of a simpler model and can facilitate parametric analysis on internal cabling. ARROW implemented this technique, solving the 3D electromagnetic model of the structural parts through a full-wave method without explicitly considering the cables and then conducting a multiconductor transmission network analysis on the cable harness. A special attention was devoted to avoid the low-frequency breakdown problem arising in typical integral equation electromagnetic solver. In particular, researchers used a formulation separating electric current and charge unknowns, while a triangular patches discrete model of the structure allowed a high fidelity simulation. In the aerospace industry that continues to seek weight reduction, use of composite materials is significantly bringing a host of benefits regarding fuel consumption and maintenance cost reductions. Given that composite aircraft are more vulnerable in lightning strikes, the newly developed tool should control and reduce such an external threat, improving aircraft safety.