Astrocytes take centre stage in the brain
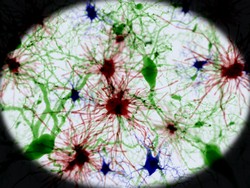
The EU-funded PLASTICASTROS (Plasticity at the tripartite synapse: an in vivo study of astrocyte-synapse interactions in the mammalian cortex) project studied the influence of astrocytes on neural networks in a living mouse. Astrocytes have thin spidery extensions that envelope neuronal synapses. Using an in silico screen, the researchers identified some 25 cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) for which the function is unknown in astrocytes. As a replacement for existing transcriptome profiling tools that are prohibitively time-consuming, the team developed an affordable, rapid and flexible system. This tool permits genetic manipulation of selected pathways in brain cells. In theory, this method should be transferable to rats for example, for which there are no suitable transgenic lines. Constructs were generated to analyse the participation of selected CAMs in signalling pathways when overexpressed. Future research plans include selective elimination of the proteins to determine their impact on astrocyte physiology, synapse structure and ultimately, mouse behaviour. The researchers worked on the waking mouse with focus on the visual cortex. They monitored calcium dynamics in astrocytes in this region of the brain. Signals during visual stimulation of the cortex revealed a spatiotemporal dynamic pattern. This pattern was distinguishable from the visually-driven component of the calcium signal in individual cells, as well as within the wider astrocyte network. In addition, these could also be separated from the signals resulting from arousal. To link physiological data with the structure of individual astrocyte processes, the scientists used correlative light and electron microscopy. After in vivo imaging, brains were processed for serial block face electron microscopy to produce high resolution 3D images. PLASTICASTROS project work has established a substantial baseline for future work on astrocyte signalling. Applications include changes in neurological diseases such as schizophrenia where information flow is affected.