Deeper understanding of human motor control and the brain
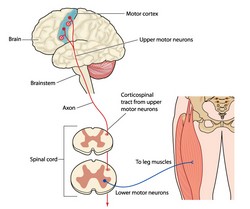
A large amount of joints and muscles provide the musculoskeletal system with much freedom. As a result, any motor task can be carried out through an endless variety of muscle activation patterns. How the brain generates appropriate muscle activation patterns is a challenging research question, considering the great complexity of the sensorimotor and musculoskeletal systems. With this in mind, the EU-funded OPT (Optimality principles in human motor control) project sought to gain deeper insight into how the brain creates a suitable muscle activation pattern given a particular movement task. By using computer simulations and a neuro-musculoskeletal model of the human arm, project partners tested the optimal control theory. The theory is a key concept in human sensorimotor control which attempts to explain how the brain copes with the many degrees of freedom. Specifically, the OPT team developed a novel optimal control musculoskeletal model of the human arm which allows the neuroscience community to examine what movements would look like in situations such as minimising energy and muscle force. It also utilised the model to predict movements while reducing costs at the muscle input, mechanical and kinematic levels. Findings show that movements made by humans are only consistent with costs at the kinematic level. In contrast, mechanical and control costs do not contribute to movement path selection by the brain. Further experiments reveal that the brain prefers muscle activation patterns that are advantageous. It does so by favouring muscles that can efficiently contribute to the positive mechanical work done. By providing explanations for how the brain needs accurate information about the state of the musculoskeletal system and about its relationship with the world around it, OPT contributed to the state of the art in the field of human movement control.