Centriole biogenesis
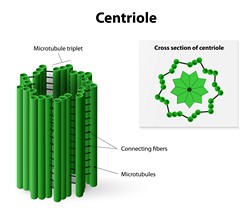
C is a cylindrical cell structure mainly made of a protein tubulin and it is found in most eukaryotic cells. C is an important part of centrosomes involved in organising microtubules in the cell cytoplasm. The position of cell organelles such as flagella and cilia associated with cell motions is determined by C, which forms the basal body. An inability of cells to use C to make functional cilia and flagella has been linked to a number of genetic and developmental defects. The mechanisms that determine C length and its involvement in the formation of cilia and flagella remain unknown. A number of centrosomal and centrosome-associated proteins (CP110, Cep97, Cep120, Cep104, CPAP, SPICE1 and centrobin) have been implicated in these processes. The overarching goal of the EU-funded CENTRIOLE_LENGTH (Molecular basis of centriole length control) project was to understand how these proteins cooperate in C and cilia biogenesis. Using a multidisciplinary approach, researchers discovered that Cep104 is a novel tubulin binding protein. Determination of the crystal structure of Cep104 provided an explanation of the interaction between its domains and tubulin. Other functional interactions of centrosomal and centrosome-associated proteins were established and characterised. These data provided new platform for further investigation of C length regulation and ciliogenesis. At the same time, researchers obtained structural and functional information about the microtubule severing enzyme katanin. Importantly, katanin has been recently implicated in the development of microcephaly. Thus, new data from the project provided important insights on katanin and katanin subunit complexes and their crystal structures.