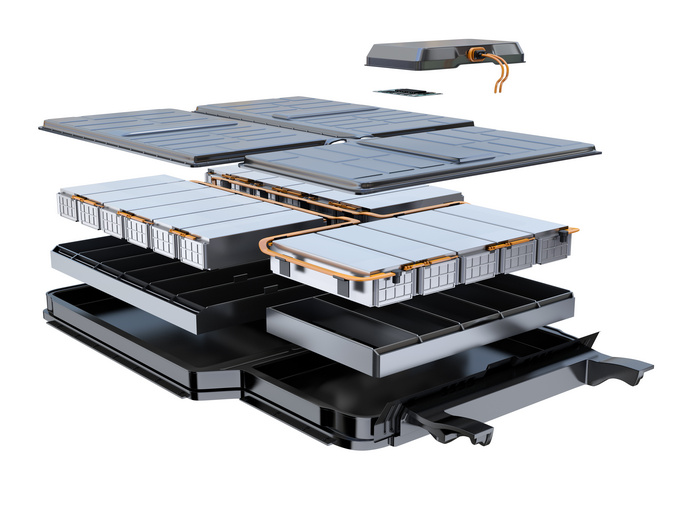
An advanced lightweight battery system for electric vehicles
The EU-funded ALBATROSS(opens in new window) project designed and tested an improved advanced battery pack that reduces drivers’ concerns about driving range and charging times. It is based on circular design principles, thereby facilitating second-life applications for repurposed used batteries and recycling. “Every level of design and operation was improved to create a full battery system concept,” explains project coordinator Aysel Pilav. “At the module level, we combined lightweight housings and high-energy cells, so the carrier tray itself contributes structurally, reducing redundant parts. Robust laser-welded busbars(opens in new window) ensure high electrical performance and durability.” Thermal management of the pack relies on partial immersion cooling, complemented by ultra-thin printed heaters and sensors embedded directly into modules. These sensors provide real-time temperature and strain data, enabling much finer control and balance during charging and discharging.
More intelligent
The new battery management system(opens in new window) (BMS) features advanced algorithms capable of early warning detection of failures, predictive safety management and flexible reuse in different pack configurations. “The BMS not only achieved voltage, current and temperature with high precision but also enabled remote diagnostics, ensuring long-term reliability while laying the foundation for second-life applications,” observes Pilav. The integration of advanced sensorisation with the new BMS has transformed pack intelligence. “With hundreds of measurement points and predictive algorithms, it became possible to detect risks earlier and manage thermal loads more effectively,” Pilav adds. Beyond pack operation, project partners also developed dismantling and recycling solutions using semi-automated robotic disassembly to recover materials and components safely and efficiently. “Eco-design principles and life-cycle assessment(opens in new window) were applied from the very beginning, so that sustainability and circularity principles guided technical choices throughout the development,” notes Pilav.
Longer, faster, safer
“ALBATROSS makes electric vehicles (EVs) more attractive and sustainable by improving energy density, enabling faster charging and enhancing crash safety,” Pilav claims. “For consumers this means longer driving ranges, shorter charging times and more reliable batteries. By extending battery life to 300 000 kms and enabling second-life use in stationary storage, the project reduces waste and lowers costs.” In addition, life-cycle assessments confirmed more than a 20 % reduction in CO2 emissions compared to existing products. “Through its advances in sensorisation, thermal management and circular design, ALBATROSS strengthens Europe’s competitiveness, delivering safer, greener and more affordable electric mobility worldwide,” states Pilav. “EU funding made it possible to bring together a diverse group of partners from across Europe, covering the entire value chain from materials and manufacturing to recycling and digital solutions,” she continues. “This diversity ensured that expertise from different fields could be combined into one BMW i3 demonstrator. Without this cross-border collaboration, integrating so many advanced technologies into a single battery pack would not have been possible”.
The future
According to Pilav, the next step for ALBATROSS is the industrialisation of the developed technologies, from lightweight pack structures to advanced sensing and predictive management. “These results will not only support future generations of EVs but also contribute to shaping standards and regulations on safety, recyclability and digital monitoring.” “In this way ALBATROSS will help Europe stay competitive in the global EV market while also supporting climate targets and sustainable mobility for citizens,” Pilav concludes.