Impact of river sediment movement
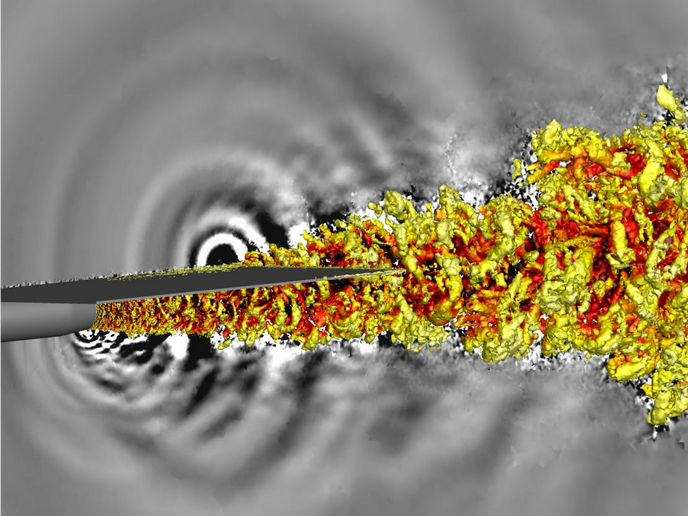
Dealing with the consequences of sediment movement and build up in European rivers and coastal systems cost EU governments tens of millions of euros each year. These high costs are partly a result of our inability to model accurately how sediment moves and is entrained. A drawback of current modelling techniques is that they do not sufficiently consider the turbulent structure of the flow nor the interactions between the flow and the sediment. The 'Numerical simulation of sediment entrainment' (CFD-DEM) project seeks to fill this void. Funded by the EU, the project is studying how turbulence affects the entrainment and movement of coarse particles on the bed of an open channel. The dynamics being investigated include drag-and-lift forces, degrees of protrusion, blocking by particles upstream, and the impact of downstream particles. CFD-DEM has already achieved a number of significant results. Among these are a novel half-distributing forcing strategy and numerical results for sediment entrainment in turbulent channel flow. This shows a close relationship between continuous particle movements and sweep events. The project also measured, for the first time, the hydrodynamic forces acting on saltating particles, as well as the particle collision process. CFD-DEM found that the mechanisms for entrainment and those for continuous saltation of grain-size particles are different. Once complete, CFD-DEM results will be very useful for those authorities charged with managing sediment build-up in rivers and other waterways, and will help them plan interventions more effectively.