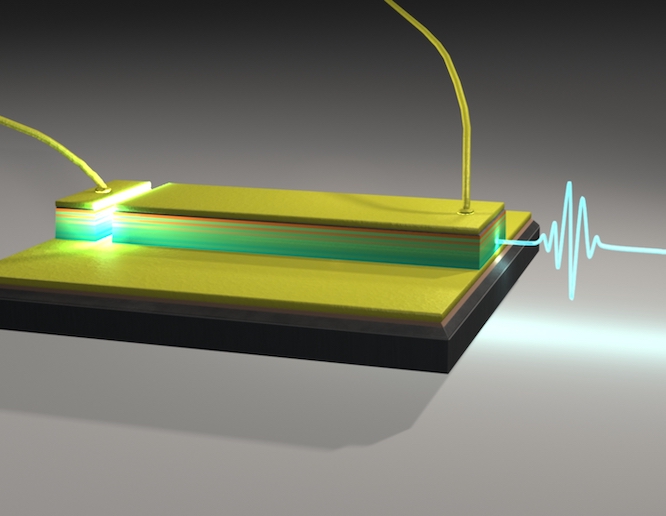
Microchip for measuring droplets electrically
MICROFLUCHIP was executed by specialists in microfluidics, bioimpedance and fabrication technology for the analysis of complex liquid samples. Researchers manufactured a microchip consisting of a microchannel for fluids flow, an impedance sensor, and a sorting or separation mechanism which employs electrode actuation switching. To improve sensitivity for the impedance sensor, elaborate electrode interface, low noise front-end circuitry, as well as signal processing methodology, were devised for measuring dielectricity of droplets. The separation electrodes were insulated with film that suppressed hydrolysis of the high voltage actuation. In addition, the microchannel and electrodes were coated with hydrophobic monolayer for enhancing the flow of the droplets. Multisinewave signals of frequencies ranging from some kHz to 10 MHz were applied on the droplets via the sensing electrodes. Bioimpedance spectroscopy was employed to measure the dielectric response of the suspended, in droplet, particles. Curve fitting and statistical analysis enabled the characterization of the suspended particles. The particles imitated dielectric characteristics of erythrocyte cells and therefore this sensor can find potential application in biosensing. Researchers successfully demonstrated the potential of droplet-based impedance measurement in analysing microparticles/cells enclosed in droplets by determining their dielectric characteristics. This is a step in the direction for electrical measurement of erythrocyte cells within a droplet bioreactor and possibly for online cell-culture discrimination in future.