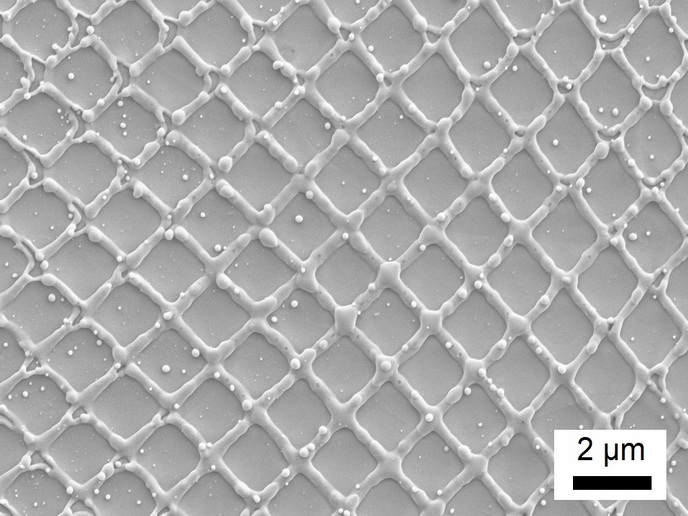
High-performance lightweight nano-reinforced alloys
The EU funded the project EFEVE(opens in new window) (Development of a new high performance material associated to a new technological energetic, flexible, economical, versatile and ecological process to make super strong and lightweight components) to develop materials and processes that will improve the functionality of automotive parts and wind systems. On the one hand, the automotive industry is tending to the design and development of smaller and more powerful engines with lower fuel consumption. This so-called engine downsizing requires components melted at higher temperatures and pressures than current aluminium casting alloys to increase both their static and dynamic properties. To this end, magnesium can play an important role as it is 35 % lighter than aluminium. The challenge is to obtain magnesium castings that meet stringent specifications and safety regulations. On the other hand, the wind energy industry is also keen to reduce the cost of electricity production through the use of lighter turbine components. The EFEVE team worked on developing such engine and turbine components based on aluminium and magnesium. Magnesium alloys were produced by squeeze casting and aluminium alloys by hybrid low-pressure squeeze casting. Both processes were evaluated at laboratory scale. The next step was to move forward toward their implementation in industrial pilot lines. Specifically, analysis has identified required changes to an existing high-pressure die casting line to enable magnesium squeeze casting. In addition, demonstrators of new equipment for aluminium low-pressure squeeze casting were designed and assembled. Lastly, researchers validated methodologies and tools for their energy efficiency and reduced material usage. Nano-reinforcements have the potential to improve the microstructure as well as the mechanical properties of the finished products. EFEVE has delivered nano-reinforcements for magnesium- and aluminium-based components needing minimum energy and raw materials for their manufacture. The developments also promise a major boost to the competitiveness of European foundries.