Psoriatic arthritis - link to health risks
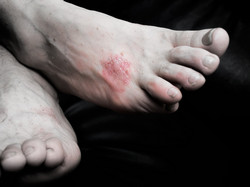
Up to 30 % of individuals that suffer from the skin condition psoriasis will develop inflammatory arthritis. Inflammation can lead to vessel damage and plaque formation, thereby comprising a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Rheumatoid arthritis patients present with twice the risk of developing heart problems, underscoring the importance of inflammation in vascular dysfunction. The primary objective of the EU-funded PACAD (Psoriatic arthritis and coronary artery disease) project was to investigate the link between psoriatic arthritis and coronary artery disease. Towards this goal, researchers used existing medical records from Iceland to compare the risk of cardiovascular disease in the general population to that seen among patients with psoriatic arthritis. PACAD characterised and compared the risk factor profiles of the two groups, focusing on cardiovascular factors. Longitudinal data analysis indicated that patients with psoriatic arthritis did not have a shortened lifespan compared to that seen in the general population. This analysis also allowed researchers to develop a fully adjusted model of cardiovascular disease, which should help future studies. Collectively, the results provide a better understanding of psoriasis-induced arthritis. This is expected to facilitate better care of such patients through palliative interventions. Frequent cardiovascular screening of psoriasis patients will also help them opt for appropriate lifestyle choices to avoid heart disease.