Small molecules for meningioma therapy
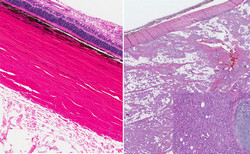
A meningioma is an intracranial tumour that forms on the meninges, the membranes that cover the brain. Albeit common, the majority of meningiomas are benign. Treatment entails surgical resection but when complete removal is not possible, patients relapse within a few years. This clearly portrays a need for medical interventions in the fight against meningioma. The scope of the EU-funded HTDDSFMT (High throughput drug discovery studies for meningioma therapeutics) project was to identify molecules that could be used as novel therapeutic strategies for meningiomas. In this context, researchers followed a high-throughput drug screening approach and screened nearly 4 000 FDA-approved drugs. The main criterion was that the bioactive compounds need to cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain. In this respect, scientists identified four compounds and determined their effective inhibitory doses on different cell lines. Based on this data, they selected two lead compounds that worked efficiently at low concentrations and proceeded to test them in a xenograft mouse model of meningioma. Mechanistic insight into the function of the SM1 compound indicated that it exerted its anti-tumour effect by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signalling and by upregulating pro-apoptotic signals. Taken together, the evidence generated by the HTDDSFMT study opened new avenues towards the development of novel therapies against meningioma. The identified compounds need to be explored further to determine their clinical benefit in human trials.