New biomarkers for colorectal cancer management.
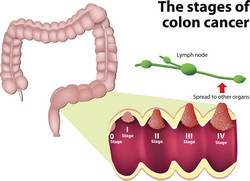
CRC has one of the highest incidences of all cancers with 1.2 million cases diagnosed annually worldwide. CRC is asymptomatic and frequently diagnosed in the later stages resulting in high mortality. CRC therapeutic agents such as fluorouracil (5-FU) and anti- epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) act to induce tumour regression through activation of cell death, or apoptosis. Advances in targeted molecular therapies have led to the addition of anti-EGFR agents to the systemic chemotherapy regime. Nevertheless, half of CRC patients do not respond to anti-EGFR treatment. Dysfunctional apoptosis is known as a key factor in chemotherapy resistance. The goal of the APO-DECIDE(opens in new window) (Apoptosis modelling for treatment decisions in colorectal cancer) consortium was to develop systems medicine tools that predict treatment responses in CRC patients. Benefits could include a change in chemotherapy regime once patient responses had been determined. APO-DECIDE created a biobank of cancer and matched normal tissues from untreated, 5-FU chemotherapy-treated and anti-EGFR therapy-treated patients from several European sites. Data were combined into a database with genetic tumour characterisation, clinical, and patient follow-up data collected for the project. Systemic evaluation of changes in cancer cell apoptosis response to chemotherapy is based on protein quantification. The APO-DECIDE team developed quantitative protein profiling platforms for clinical application-based on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples. These platforms utilise previously validated reverse phase protein-lysate array technology and digital immuno-histopathology. Systems modelling using these platforms identified high variability in individual patients in activation of caspases, the critical enzymes in apoptosis induction. As a result, the project developed a tool to identify stage III CRC patients who will respond to 5-FU-based chemotherapy and those who will not, and may require additional targeted therapies. APO-DECIDE also investigated the ability of systems modelling to predict the impact of anti-apoptotic antagonists on the induction of apoptosis in CRC. Research data proved the potential of these antagonists in combination with 5-FU-based chemotherapy. Results obtained with human CRC cells in mouse models indicated that the anti-apoptotic antagonists led to a reduction in tumour cell survival. APO-DECIDE successfully developed the infrastructure for future clinical research and the treatment strategy for the CRC. It also demonstrated proof-of-concept for the application of virtual clinical trials for the clinical trial design.