Muscle insulin resistance in diabetes
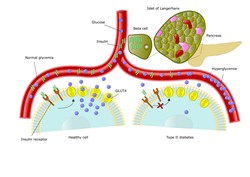
In type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance leads to reduced glucose uptake by muscles. Accumulating evidence indicates that the accumulation of molecules such as collagen and hyaluronan outside the muscle cells poses a significant barrier to glucose uptake through the extracellular matrix (ECM). Current therapeutic options are limited because of an incomplete understanding of the underlying pathophysiology. To address this, the EU-funded EMRAMIR (Extracellular matrix remodeling and muscle insulin resistance: role of hyaluronan-CD44 interaction) project set out to study the interaction of hyaluronan with the CD44 receptor in regulating muscle insulin resistance. Previous work by the consortium had shown a hyaluronan content increase in the skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant mice, which upon normalisation reversed the resistance phenotype. During EMRAMIR, scientists observed that genetic deletion of CD44 did not affect insulin sensitivity in mice on a low-fat diet, but muscle insulin resistance increased on a high fat diet. Combined with other experimental data, these observations suggested that increased insulin signalling and muscle capillarisation might be responsible for higher insulin resistance in the absence of CD44. Overall, the EMRAMIR work suggested that a high fat intake leads to a previously unrecognised change in the physical structure of the environment surrounding muscle cells. This reduces muscle capacity to respond to insulin causing various complications. The functional link between hyaluronan and CD44 interaction in the regulation of muscle insulin resistance opens new avenues for research in the field. Further insight into the molecular mechanism of this association should help identify novel targets and develop novel therapies.