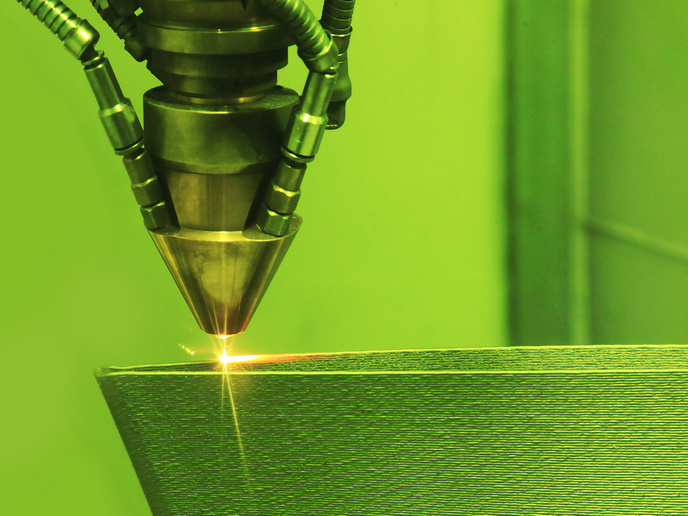
Quality control for laser metal deposition
LMD technology has major benefits, including almost complete elimination of material waste during manufacture. It also enables the easy machining of less dense materials, such as aluminium or titanium compared to steel. The EU-funded project INTRAPID(opens in new window) (Innovative inspection techniques for laser powder deposition quality control) developed three NDT methods for inspection of parts and components manufactured by additive manufacturing processes, in particular LMD. They were based on laser ultrasonics, eddy currents and laser thermography for surface distortion measurement. Each method was based on a different physical principle and tested very small component areas, which could therefore be adapted to test parts of any shape or size. The project commenced with the successful production of requirements' specifications and the manufacture of reference samples using high-brightness electron beams. Test samples with natural flaws were also manufactured based on selected parameters. The three NDT methods were optimised through modelling as well as practical and experimental data. Laser ultrasonics modelling helped establish the surface displacement amplitudes and other parameters for the reference samples. The results were validated by experimental outcomes. Modelling the eddy current method revealed that a lower sensitivity for embedded defects would be obtained for smaller diameter coils. To overcome this limitation, researchers developed impedance matching circuits and a procedure for the manufacture of small coils. LMD technology was successfully used in repair, coatings, hybrid build and 3D near-net shape manufacture of small intricate parts. Enabling reliable QC through NDT will increase LMD applications for the manufacture of specialised components, particularly in the automotive, aerospace and medical implant industries. Currently casting and forging markets are worth billions globally, with a steady market growth of 10-15 % per annum. Successful project outcomes will therefore improve the competitiveness of the participating small and medium-sized enterprises thanks also to significant waste and energy reduction during manufacture.