Europe, Japan on gravitational astronomy
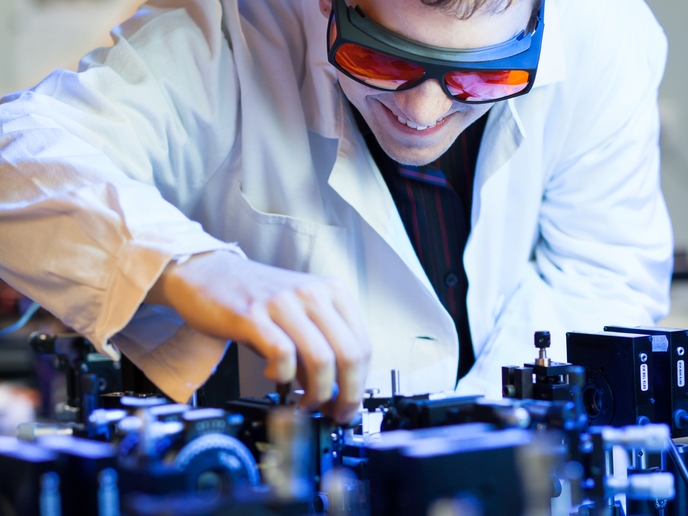
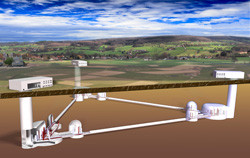
Advanced detectors and third-generation observatories will soon offer the possibility to perform gravitational wave observations, allowing astronomers to peer into the most violent places in the universe. To this end, the ET and KAGRA are focusing on common technologies for gravitational wave telescopes, with special focus on cryogenics, and mechanical and optics topics. The EU-funded project ELITES (ET-LCGT telescopes: Exchange of scientists) was initiated to boost scientific collaboration between the two. Together, European and Japanese researchers worked on the design and development of the cryogenic suspension prototype of KAGRA, one of the most difficult and challenging components of this detector. Sapphire fibres for suspending the KAGRA mirrors were tested and found to be compliant with the stringent requirements. Detector sensitivity is mainly limited by thermal noise associated with mirror substrates, their reflective coatings and suspension elements, as well as by noise resulting from the quantum nature of the light used in sensing. Project research thus targeted investigating the mechanical behaviour of complex optics structures used as reflecting surfaces in gravitational wave detectors. Scientists directed work based on past results regarding mechanical losses in dielectric coatings in cryogenic conditions. Further studies on optical components including the long filter cavities for optical squeezing designs were also conducted. Another part of ELITES work was geared towards the development of new assembling technology like silicate and indium bonding. Dissemination and outreach activities to schools, cultural institutions and the general public were very strong. ELITES significantly contributed to establishing two-way relationships between Europe and Japan with exchange of know-how and intense research and development activities in gravitational astronomy.