Higher profile for neglected zoonotic diseases
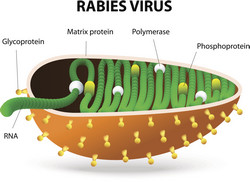
Twenty-one African and European partners joined forces to develop suitable interventions for eight neglected zoonotic diseases (NZDs) under the EU-funded project ICONZ(opens in new window) (Integrated control of neglected zoonoses: Improving human health and animal production through scientific innovation and public engagement). The consortium's aim was to develop integrated control packages for the diseases anthrax, bovine tuberculosis, brucellosis, cystic echinococcosis, porcine cysticercosis, leishmaniasis, rabies and zoonotic trypanosomiasis. Partners successfully completed a baseline sample collection of over 22 000 animals and most of the data analyses in all 7 African International Cooperation Partner Countries (ICPCs). These were used as input for the field-based case studies along with the sociological research methodologies and epidemiological studies that were developed. As a result, ICONZ is the first multidisciplinary large-scale study undertaken across Africa on NZDs. Researchers developed and tested methodologies to assess the socioeconomic burden arising from these eight zoonotic diseases and the findings were published in journals and presented at international conferences and workshops. They also identified risk factors and created a knowledge base on best practices in order to develop cost-effective and appropriate intervention strategies and protocols. ICONZ collaborated with another EU-funded project, DISCONTOOLS, and developed an inventory system for all eight zoonoses. It comprises details such as diagnostic tools, treatment and policy recommendations for each of the diseases and regular data updates. Diagnostic and quality assurance tests for these diseases were successfully conducted. Project members also developed a database cataloguing all relevant research and publications as well as funding sources for the zoonosesofinterest. Regarding dissemination, and besides the project website, outcomes were presented at international meetings and conferences, and published in eight issues of the ICONZ magazine in English and French. The successful last international meeting of the project was held in Geneva in 2014 and co-hosted together with the World Health Organisation (WHO), the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) in collaboration with ADVANZ, another EU-funded project addressing NZDs. ICONZ also participated in high-profile events such as the One Health congresses in Melbourne (2011) and Bangkok (2013). One reason for the neglect of NZDs has been their lack of political power to attract the attention of national governments and donors. The work by ICONZ will help explain NZDs and their epidemiological and economic impacts to decision-makers, thereby creating a critical mass to raise their profile. The wider recognition of NZDs will also address the problems of under-reporting and misdiagnosis.