Re-using industrial waste heat
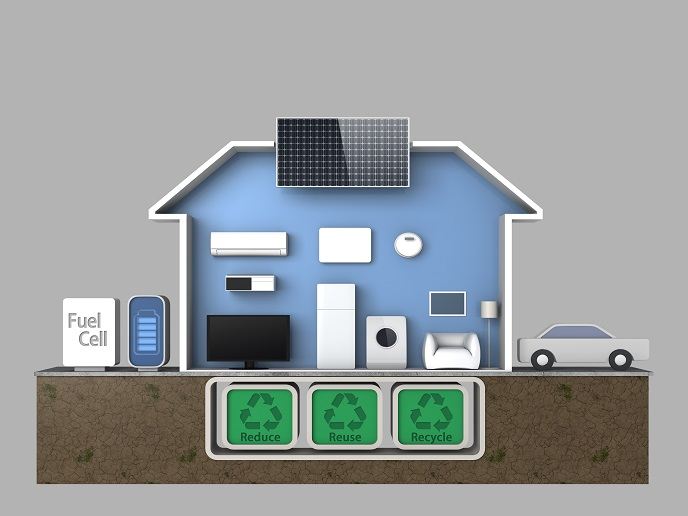
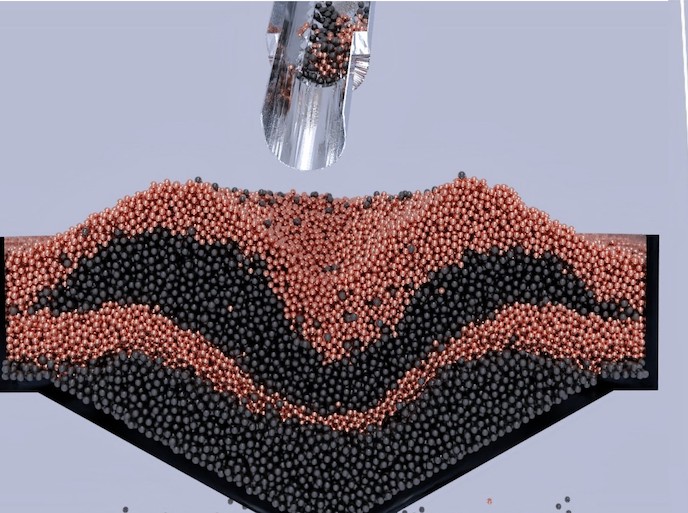
Nearly 50 % of Europe's energy demand stems from heating needs. The EU-funded project HEAT SAVER developed a novel thermochemical heat storage system to help meet that demand by storing and releasing waste heat from combined heat and power (CHP) production, solar heating and other industrial sources. The technology relies on a reaction pair consisting of water and zeolites. In the storage mode, incoming heat is used to dissociate the zeolite bound to water. To recover the heat, the pair is allowed to react again at the desired temperature such that the heat stored as chemical energy is released. Researchers custom designed all sub-systems, including the external heat exchangers, sensors and control system. The heat exchanger has been optimised for efficient heat transfer with an innovative concept that enhances water vapour flow through the storage material (zeolites or zeolite-type materials). In addition, it uses significantly less materials and less storage volume compared to other comparable heat exchangers on the market and is cost effective and easy to manufacture as well. The up-scaled system is portable and boasts a 1 000-litre storage volume and the potential to achieve 3 to 10 times higher specific storage densities than water. HEAT SAVER technology re-uses waste heat to balance fluctuating energy demands and increase the efficiency of industrial processes. As a sustainable alternative energy resource, it reduces environmental impact while enhancing independence from fossil fuels, in line with EU goals and philosophy.