Multiple sclerosis — immune dysfunction
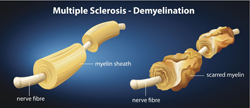
In MS, nerve signal transmission is hampered, causing symptoms such as physical and mental dysfunction. Understanding how the immune system malfunctions and attacks the myelin fibres that insulate neuronal cells is key to developing effective treatment.Central to adaptive immunity and antigen presentation are two sub-populations of T lymphocytes, namely helper T cells and regulatory T cells. These cells finely modulate the immune system by activating or supressing other immune cells.A fine balance among helper and regulatory T cells is essential for physiological immune function. Scientists of the EU-funded IMMUNO BALANCE MS project decided to investigate these two cell populations in MS. The key objective was to elucidate early mechanisms that drive such equilibrium between the inflammatory and immune-suppressive response in MS.To this end, researchers analysed the ability of specialised antigen-presenting cells known as dendritic cells (DCs) from MS patients to functionally interact with T cells. When compared to cells from healthy controls, DC sub-populations from MS patients were altered in frequency, indicating a skew in the immune system.Although no visible differences in cytokine production were observed, global transgene expression analyses revealed significant molecular differences. In particular, in MS patients an abnormal induction of T cell responses was seen. This was accompanied by a tendency of MS DCs to drive inflammation at the expense of regulatory T cell activation.Taken together, the results of the IMMUNO BALANCE MS study underline the importance of the balance between inflammation and immune regulation in MS. Delineation of the mechanisms that regulate this tuning could be exploited as a therapeutic approach for MS.