Biomarkers for bladder cancer
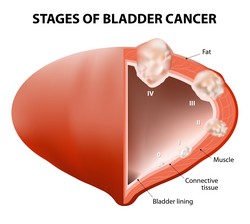
Bladder cancer (BC) causes 165 000 deaths per year worldwide. As current treatment options are limited, there is a need to gain a better understanding of disease biology to design novel therapeutic strategies. To achieve this, biomarkers are required that can be associated with disease stage and implemented to monitor the outcome of therapy. The EU-funded BCMOLMED(opens in new window) (Molecular medicine for bladder cancer) project has used omics technologies to identify biomarkers for bladder cancer. A combination of urinary biomarkers with cytological examination revealed more than 100 urinary peptides differentially excreted between patients with recurrent BC and patients without a sign of recurrence for at least a year. These significant results were published in Nature Reviews Urology. Investigations into the role of proteins revealed that levels of NRC-interacting factor 1 (NIF-1) and histone 2B (H2B) in the urine from patients with benign urological diseases significantly differed from that of patients with bladder cancer. NIF-1 showed decreased tissue expression levels as BC cancer progresses from non-muscle invasive BC to muscle invasive BC, while H2B presented the opposite trend. Results appeared in the Journal of Proteome Research. Down-regulation of profilin-1 decreased cell adhesion as well as tumour growth. Additionally, silencing of this protein resulted in the decreased expression of other proteins associated with the non-canonical Wnt/Ca2+ signalling pathway, important in the development of many cancers. Knockdown of another two proteins in the cell lineT24M resulted in the inhibition of cell migration and proliferation. Additionally, significant decrease in tumour growth was noted upon silencing one of the molecules. A manuscript is in preparation. In total, the BCMOLMED BCCluster knowledge base integrates data from 112 published manuscripts, and almost 1 600 statistically significant features associated with BC invasion. Additionally, 435 protein-protein interactions and 92 molecular pathways significant in BC invasion were deposited in this database. Early stage researchers under the BCMOLMED umbrella received extensive training, enhancing their competitiveness in the field. The long-term goal is to ensure the expertise of the next generation of researchers in biomarker and drug target discovery.