Resumption of successful DNA replication at stalled forks
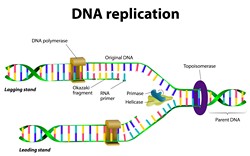
Stalling at replication forks caused by interference with progression, stability and restart can induce cancer. Smc5-Smc6 is a multi-subunit complex that is responsible for the progression of replication forks through damaged DNA and is recruited to forks that collapse. The project CHROMOSOME STABILITY (Coordination of DNA replication and DNA repair at single-forks: the role of the Smc5-Smc6 complex in replication fork stalling and resumption) identified sites of post-translational modification by part of the Smc5-Smc6 machinery. The researchers looked in particular at the small ubiquitin-like modifier SUMO that is dependent on a sub-unit of Smc5-Smc6, Nse2. SUMO is involved in post-translational modification. SUMO targets identified by the team include Scc1. Research results show that Scc1 SUMOylation by Nse2 is required for repair of a DNA double strand break. Another target Sgs1 is significant for its role in a human cancer called Bloom Syndrome. Data confirmed Sgs1 is involved in the fixing of recombination intermediates at damaged or stalled forks. Unexpectedly, the researchers also discovered a change in the DNA winding status at compromised forks. As failure to repair and restart replication errors at forks can lead to various cancers, knowledge of the molecular machinery could lead to new therapeutic targets. A personalised approach at this level promises to reduce highly unpleasant side-effects and increase therapeutic efficacy.