The first swallowable light-emitting capsule for eradicating Helicobacter pylori
According to the WHO, H. pylori is considered a class I carcinogen agent responsible for nearly 90% of gastric cancer cases. Standard therapy consists of a combination of antibiotics and antisecretive drugs, which leads to up to 30 % antibiotic resistance in European countries prohibiting cure despite several treatment cycles.
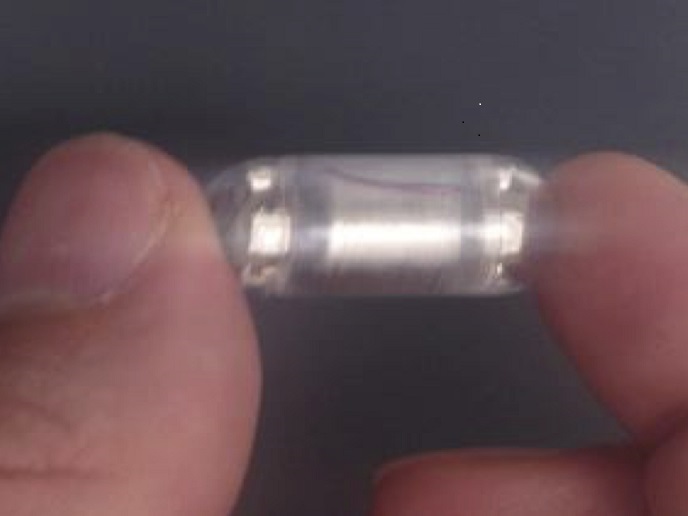
A light-illuminating device for treating H. pylori
To address this issue, the EU-funded Capsulight(opens in new window) project developed a novel therapeutic strategy based on photodynamic therapy. Based on the absorption of light by specific molecules in the bacteria called porphyrins, these then produce toxic chemicals that kill the microbes. “Our approach is based on the concept that similarly to chemical and pharmacologically active molecules, photons can serve as healing agents,″ explains project coordinator and Probiomedica Chief Technical Officer, Giovanni Romano. The idea of a therapeutic ingestible and light-emitting pill was conceived by merging research and know-how in the field of photonics/phototherapy (University of Florence) and robotics for device miniaturisation (Sant’Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa). The device is based on the established technology and safety of endoscopic capsules for diagnostic use. Capsulight is a small ingestible capsule, as small as an antibiotic pill, that emits light at specific wavelengths suitable for killing bacteria. It contains a battery and an electronic board to drive the source of 3-colour LED light and an outer transparent casing. It also contains pH and temperature sensors for safety. The capsule is designed to switch off once passing into the intestine so as not to harm the intestinal flora. Capsulight has undergone several tests for its light-emitting properties and its resistance under harsh laboratory conditions that mimic the gastric pH. Researchers have also tested the integrity and safety of the capsule in a non-infected minipig animal model with no side effects. In vitro tests have demonstrated 97 % efficacy in killing the bacterium, per pill-emitted light.
Capsulight advantages
Endoscopic devices that illuminate the gastric cavity are available as alternative treatments for H. pylori infection. However, these are limited to very few clinical pilot trials and their invasive nature restricts patient compliance. “Capsulight administration is as easy as swallowing a pill,″ emphasises Romano. At the same time, the use of light instead of pharmacological agents minimising drug-related side effects, is expected to reduce antibiotic resistance and the associated healthcare costs. Most importantly, it can be used to treat infected patients that have developed resistance to antibiotics.
Future directions
The next step for Capsulight partners is to assess the therapeutic efficacy of the device, in a pilot clinical trial followed by a multicentre clinical trial in Europe. They will also proceed to certify the device and conduct business feasibility studies. According to Romano, ″the Capsulight project has provided the necessary knowledge on the framework of stakeholders implicated in commercialisation of the product.″ Partners are ready to approach the market and participate in future Accelerator Pilot calls (H2020) while efforts to develop and enlarge the network of clinical research organisations, medical centres, component production companies and product distributors, are ongoing.