Sinus surgery stent improves patient outcome
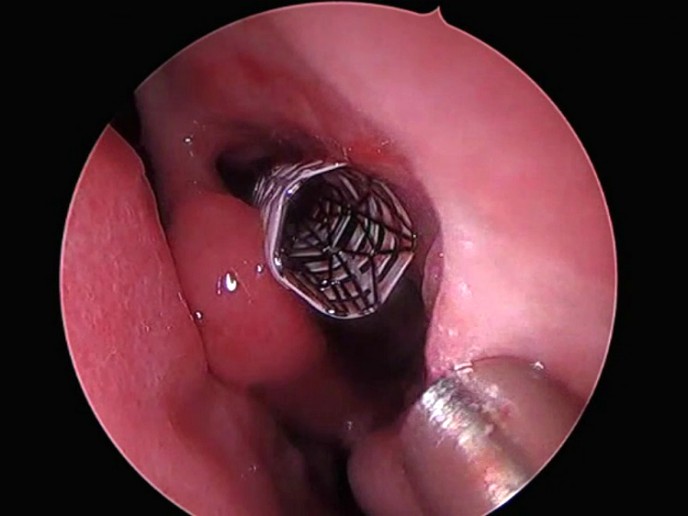
Under physiological conditions, paranasal sinuses produce mucus necessary for the nasal passages to work effectively. In chronic sinusitis, sinuses are inflamed and patients experience nasal congestion, facial pressure, headaches and fatigue. In 20 % of the cases, breathing becomes impaired, requiring patients to undergo functional endoscopy sinus surgery (FESS). However, post-FESS healing is often suboptimal with 23-47 % of patients requiring revision surgery. An innovative stent design To reduce post-surgery complications and improve FESS outcome, the EU-funded STstent(opens in new window) project designed the composite ArchSinus stent to be implanted after surgery. As Lena Shlossberg, Clinical & Regulatory Affairs Manager at STS Medical explains, “the idea was to keep sinus passages open after surgery to promote optimal healing.″ ArchSinus is composed of a polyurethane outer cover and an inner nitinol alloy body, enabling it to conform to nasal geometry and anatomy while resisting the pressure of the swelling mucosa. This combination of materials prevents stent diameter reduction and subsequent migration at body temperature. The ArchSinus stent is precisely implanted upon a balloon catheter. Shlossberg notes that “it is biologically inert, doesn’t cause any mucosal irritation and thus patients don’t feel it.″ Importantly, it facilitates local delivery of standard medication until complete post-operative healing is achieved. Lowering the stent temperature with cold saline causes nitinol softening, facilitating the stent removal. Stent removal can be performed as an in-office procedure, without anaesthesia up to 28 days after implantation. Clinical prospects The ArchSinus stent has been tested in a sheep model and has demonstrated safety and efficacy in a clinical study. Following FDA clearance in 2017, more than 60 stents have been implanted in the United States with good therapeutic results. During the STstent project, STS Medical completed a full analysis of the technical and business potential of the ArchSinus device, outlining the financial and infrastructure requirements for achieving global sales. With an overall objective to become the foremost global supplier of stent technologies for treatment of prevalent nasal conditions, STS Medical is currently working towards scaling up the manufacturing process. The feasibility study also evaluated the regulatory requirements for introducing the ArchSinus stent into the European market. The company has secured the interest of six healthcare providers – both in Europe and the United States. In addition, they have identified the optimisation work and activities required for clinical validation. Two medical centres will serve as recruitment and validation sites during the Phase 2 innovation project to obtain clinical approval. The ArchSinus stent is a short-term solution that allows the sinus to heal after a FESS operation. “Even though it is not a drug eluting implant, it promotes faster and optimal post-surgical healing than the standard of care treatment,″ emphasises Shlossberg. Implementation of the device is expected to improve the outcome of FESS procedures worldwide and substantially reduce the healthcare costs by reducing the need for revision surgeries. At the same time, this will increase patient comfort, ameliorate post-operative side effects and improve their quality of life.