A breath analysis test avoids antibiotic misuse
Accumulating evidence indicates that the emergence of resistant bacterial strains can be attributed to the injudicious use of antibiotics. Without effective antibiotics, the success of major surgery and chemotherapy can be compromised. Antibiotics active against gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli are difficult to develop since these bacteria have effective barriers against drugs.
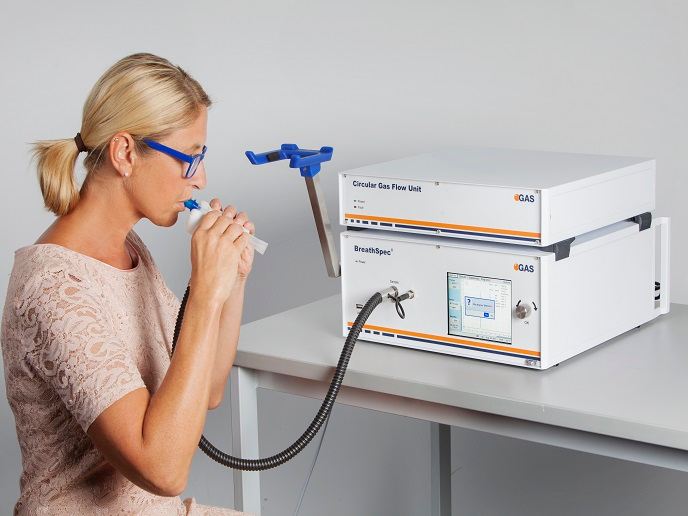
A device for breath analysis
To address this issue, the EU-funded BreathSpec(opens in new window) project developed an innovative breath test for the accurate diagnosis of respiratory tract infections. “Our goal was to determine the breath signature of patients who do not require antibiotic prescriptions,″ explains project coordinator Emma Brodrick. The Breathspec® device uses gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry, or GC-IMS, for the identification and quantification of key signature volatiles present in exhaled breath associated with the presence of bacteria. The device allows non-invasive point-of-care analysis while you wait. This provides the clinician with diagnostic results at the time of appointment, which in turn avoids unnecessary antibiotic treatment. “The most important aspect of Breathspec® is that it gives the prescribing clinician the confidence to not prescribe antibiotics,” emphasises Brodrick. During device development, partners conducted multicentre studies using patients with known pathologies to obtain characteristic data for the generation of algorithms to separate bacterial from viral infections. They also optimised the design towards a lighter, more patient-friendly breath sampler. The device was validated in over 1 200 patients with suspected respiratory tract infections from both community and hospital clinical settings. Patients found the device comfortable to use and similarly, positive feedback on Breathspec® performance was obtained from doctors and nurses.
Impact of the Breathspec® device
The BreathSpec project has pushed the boundaries of cutting-edge technology by translating lab-based volatile organic compound analysis into a point-of-care solution to the global problem of antimicrobial resistance. Currently, it is the only portable commercially available breath analyser capable of robust deployment at the bedside for trace analysis. Use of the Breathspec® device is likely to reduce antibiotic prescribing by over 30 % with respect to respiratory tract infections. This is well in excess of the projected target of the United Kingdom’s government for reducing the use of antibiotics in humans by 15 % by 2024. The next steps are to CE mark Breathspec® as an in vitro diagnostic device and validate the pilot study findings in a randomised controlled trial. This will see adoption of the Breathspec® device as a diagnostic test for respiratory tract infection, within the healthcare setting, in less than 5 years. Considering that only two new classes of antibiotics have been brought to the market in the last 30 years combined with the growing epidemic of antimicrobial resistance, there is a pressing need for effective solutions. “This is a very exciting time for IMSPEX(opens in new window). Developing a non-invasive breath test for improved antibiotic stewardship in the fight again antimicrobial resistance is truly inspiring,” Brodrick concludes. Importantly, the device will help reduce the number of community-acquired pneumonias and the high cost incurred by subsequent hospitalisation.