New weapons for fighting drug-resistant bacteria
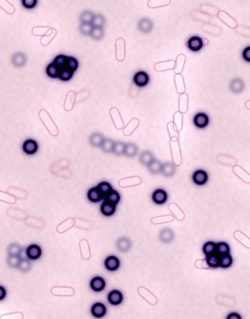
Over recent decades pharmaceutical companies have focused on developing variations of existing drugs, with the result that the number of compounds acting on new targets has been reduced. However, derivatives of existing drugs cause bacterial resistance to develop much faster than with completely new compounds. In addition, research into new antibiotics takes a great deal of time and money and profits are low. As a result, the pharmaceutical industry has shown only limited interest in developing new compounds. The EU-funded ‘Novel antimicrobials from endophytes of northern medicinal plants’ (TEJAM) project took a fresh approach to combating the threat of bacterial resistance by testing new high throughput techniques for screening internal plant microbes known as endophytes. Endophytes found in two species of shrubs, Marsh Labrador Tea (Rhododendron tomentosum) and Heather (Calluna vulgaris), were isolated by scientists and cultured in different types of growth media. The cultures were then tested for the production of antibacterials and antioxidants. Researchers also studied endophytes found in the black crowberry (Empetrum nigrum) in order to identify an antibacterial protein. The bacteria Staphylococcus aureus was used as a target organism for screening genetic copies, known as 'clones', for antibacterial properties. A unique clone that demonstrated antibacterial activity was found. The success of the TEJAM project will help overcome the problem of antibiotic resistance through new methods that can identify compounds for fighting disease and help save countless lives around the world. Therefore, the initiative will have a significant impact on the quality of life of people living within the EU as well as beyond its borders.