Molecules responsible for resistance to liver cancer therapy
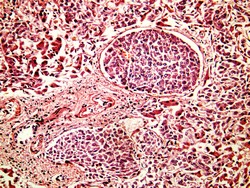
Current therapies for HCC are limited and mostly ineffective, largely due to chemoresistance. Researchers with the VEROMIRNA (miR-483-3p and drug resistance in hepatocarcinoma) project focused on microRNA-483-3p (miR-483-3p), a well-known liver cancer causing gene, to find alternative therapies that avoid this drug resistance issue. The impact of miR-483-3p is due to its target gene BBC3/PUMA, a pro-apoptotic gene often down-regulated in cancers. The scientists based their research on the fact that some chemotherapeutic agents could lower the expression of this miR. VEROMIRNA results showed that expression of miR-483-3p is regulated by cell glucose availability via an enzyme (O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase) that stabilises factors activating miR-483-3p, depending also on the presence of a glucose metabolite. Moreover, the inhibitor of glycolysis 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) reduced miR-483-3p expression in HCC cell lines. However, in vivo data showed that, the glycolysis inhibitor was not able to enhance the effect of the chemo agent 5-fluorouracil as all the tumours generated showed increased miR-483-3p expression. These findings are in line with the possibility that selective pressures lead to expansion of resistant clones with higher expression of miR-483-3p. Moreover, researchers looked at HCC cells with high availability of glucose, expression of BBC3/PUMA and steady activation of miR-145-5p (a known tumour suppressor). Results showed a strong selection of clones resistant to apoptosis through upregulation of miR-483-3p. Significance of the results in terms of clinical translation and exploitability are promising. The researchers concluded that miR-145-5p therapy should be used in parallel with simultaneous inhibition of miR-483-3p. The tests involving glucose availability suggest that 2-DG should be used for non-tumour cirrhosis as a preventive measure. Post project, two VEROMIRNA scientists are contributing to the development of an independent laboratory with nine researchers from other labs. The project also resulted in flourishing collaborations at several laboratories at the University of Chieti.