Dissecting the mechanism of sudden cardiac death
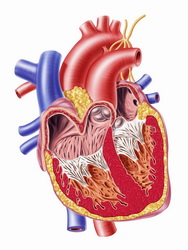
Ventricular arrhythmias are a heterogeneous group of conditions characterised by abnormal electrical activity in the heart. This can lead to cessation of heart beating and sudden cardiac death. Currently there is no treatment due to the poor understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying these conditions. For the cardiac muscle to contract normally, calcium channels known as ryanodine receptors (RyR) must pump calcium ions intracellularly. Recent evidence suggests that dysfunction in the calcium release channel is implicated in arrhythmogenesis and sudden death and in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT), a stress-induced cardiac condition. The 'Control of intracellular calcium in arrhythmias' (Contica) project investigated the role of the RyR2 receptor and calcium-dependent mechanisms in inherited and acquired heart rhythm disturbances. Experiments on human heart tissue and unique animal models unravelled important insights into the mechanism of CPVT at the molecular, cellular and whole organism level. Additionally, a large cohort of CPVT patients was studied and novel genetic abnormalities were discovered and characterised. New methods for detecting arrhythmias were developed alongside novel drugs that were evaluated for their potential to treat CPVT. The Contica project drew significant media coverage raising awareness in the general public and the scientific community on sudden cardiac death and its underlying causes. Overall, the study results will significantly improve the diagnosis of fatal arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac death and contribute to the development of novel therapeutic regimes.