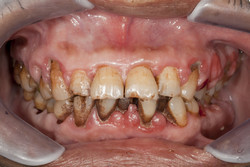
Gum disease and rheumatoid arthritis
RA is an autoimmune disease associated with chronic inflammation in the joints, causing severe pain and disability. Interestingly, the majority of patients have antibodies against proteins that have undergone a type of post-translational modification known as citrullination. In addition, RA patients have more chance of developing PD. A number of studies support a strong association between these two diseases. Scientists on the EU-funded GUMS AND JOINTS (Protein citrullination as a link between periodontal diseases and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and target for development of novel drugs to treat RA) project investigated if the bacteria responsible for PD express higher levels of the enzyme that catalyses citrullination. Peptidyl-arginine deiminase (PAD) from Porphyromonas gingivalis (PPAD) may therefore provide the link between RA and PD. Researchers performed a multidisciplinary investigation on the immune responses and susceptibility factors in both diseases. They recruited patients and healthy subjects and found elevated antibodies to the virulence factor arginine gingipain in serum samples of PD patients. Biochemical evaluation of PPAD activity indicated a strong capacity to citrullinate any protein that contains an arginine amino acid, including proteins of the immune system. Researchers determined the structure of PPAD using crystallisation of recombinant protein, which resulted in the development of specific inhibitors. In addition, several inhibitors for human PADs have been characterised. Linking a Finnish trial cohort to the Swedish dental health registry, it was discovered that age and smoking also constitute risk factors for periodontal disease in RA patients and controls. Dissemination included 77 peer-reviewed articles, 44 poster presentations, 86 oral presentations and a workshop in Poland to target the scientific world. For the public at large, there were five magazine publications and coverage on a popular television programme. GUMS AND JOINTS research has emphasised the importance of regular dental care to prevent gum disease and act as a prophylactic against RA. Moreover, other lifestyle factors may have an input such as smoking. Health authorities, medical practitioners and the public in general could help to reduce the incidence of RA, help alleviate pain and improve life conditions particularly in the elderly, and reduce the massive financial burden of this disease.